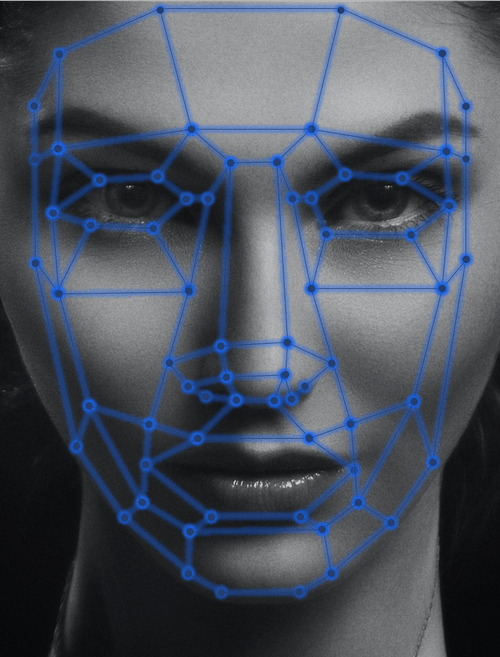
Facial Recognition System
Connecting the dots…

Connecting the dots…
A facial recognition system is a way to identify people based on their facial features; it is basically software that is based on the concept of 'recognition'.
In simple words, a facial recognition system is a way of identifying a human face using biometrics technology, which have a mapping facial features from a photograph or video and then compares the information to a database of known faces to find a match. Facial recognition is fast and very effective verification software.
Facial recognition technology is taking the world by storm, it has matured from a niche biometric proof-of-concept to one of the most widely used cybersecurity and authentication ways in the world. It is faster and more convenient than other biometric technologies, such as fingerprints or retina scans.
Face recognition systems are a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that mimics the human ability to recognise human faces. Facial recognition software, like human recognition, captures facial features and creates a pattern of facial features that it uses to identify or group a face.
All facial signatures and facial images in transit or at rest use AES-256 encryption, and no data is passed over the Internet if run on premises. Privacy is thoughtfully addressed from the full suite of administrative tools - including easy opt-in/opt-out capabilities - to the Implementation Best Practices.
The software adheres to The Australian Privacy Act 1988 (Privacy Act), which is the principal piece of Australian legislation protecting the handling of personal information about individuals. This includes the collection, use, storage and disclosure of personal information in the federal public sector and in the private sector.
The 99.87 percent accuracy is balanced by industry-leading performance that delivers results 3-5 times as fast as competing facial recognition system algorithms. The database is optimized for rapid matching against millions of records in near real time, making identification extraordinarily fast. With edge intelligence, detect a face moving through live video and create recognition in under 100 milliseconds.
Tested by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the algorithm tested as both the fastest and most compact among algorithms for wild images with less than 0.0335 False Non-Match Rate (FNMR). Increased sampling increases accuracy. The superior accuracy achieved is also a result of a greater diversity in the data set and the use of only real faces (vs. simulated faces) to train the algorithm.



Tested by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the algorithm tested as both the fastest and most compact among algorithms for wild images with less than 0.0335 False Non-Match Rate (FNMR). Increased sampling increases accuracy. The superior accuracy achieved is also a result of a greater diversity in the data set and the use of only real faces (vs. simulated faces) to train the algorithm.